Introduction
The medical device industry faces a critical choice when manufacturing implants, surgical tools, and diagnostic components: traditional investment casting or modern 3D printing? With over 15 years of supplying FDA-approved implants, we present a data-driven comparison to help engineers and procurement specialists make informed decisions.
Factor 1: Material Performance & Biocompatibility
1.1 Approved Materials Comparison
| Property | Investment Casting | Metal 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steels | 316L (ASTM F138) | 17-4PH (limited) |
| Cobalt-Chrome | ASTM F75 | CoCrMo (DMLS) |
| Titanium | Grade 23 (ELI) | Ti6Al4V (ELI) |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8-3.2μm | Ra 6.3-12.5μm |
Critical Insight:
Cast 316L shows 40% higher fatigue strength than printed equivalents due to isotropic microstructure (per ISO 10993 fatigue tests).
Factor 2: Precision & Feature Capabilities
2.1 Dimensional Capability Matrix
| Parameter | Investment Casting | DMLS/SLM |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Wall | 0.5mm | 0.3mm |
| Hole Diameter | 1.0mm | 0.5mm |
| Tolerance | ±0.075mm/25mm | ±0.1mm/25mm |
| Internal Channels | Limited | Excellent |
Case Study – Orthopedic Screws:
- Casting: Achieved M1.6 threads with ±0.02mm pitch accuracy
- 3D Printing: Required post-machining due to stair-stepping
Factor 3: Regulatory Compliance Pathways
3.1 Validation Requirements
| Certification | Investment Casting | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|
| FDA 510(k) | Established protocols | Emerging standards |
| ISO 13485 | Full material traceability | Powder lot tracking |
| ASTM F2924 | Not applicable | Mandatory for DMLS |
Time-to-Market Impact:
- Casting validation: 3-4 months (using historical data)
- AM validation: 6-8 months (requires new process validation)
Factor 4: Economic Viability by Volume
4.1 Cost Breakdown (Titanium Spinal Cage)
| Volume | Casting Cost | DMLS Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 100 pcs | $220/unit | $185/unit |
| 1,000 pcs | $105/unit | $150/unit |
| 10,000 pcs | $68/unit | $130/unit |
Tooling vs. Machine Time:
- Casting: $8,000-$20,000 tooling (amortized)
- DMLS: $120-$180/hour machine time
Factor 5: Post-Processing Requirements
5.1 Surface Treatment Comparison
| Process | Casting Workflow | AM Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Defect Removal | Ceramic shell removal | Support removal |
| Surface Refinement | Electro-polishing (Ra 0.4μm) | HIP + Bead blasting |
| Critical Step | Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) | Stress relieving |
| Validation | 100% fluorescent penetrant | CT scanning ($250/part) |
Biological Contamination Risk:
- Casting: Near-net shape = less machining = lower endotoxin risk
- AM: Powder reuse increases contamination potential (per FDA guidance)
Decision Tree: When to Choose Which Process?
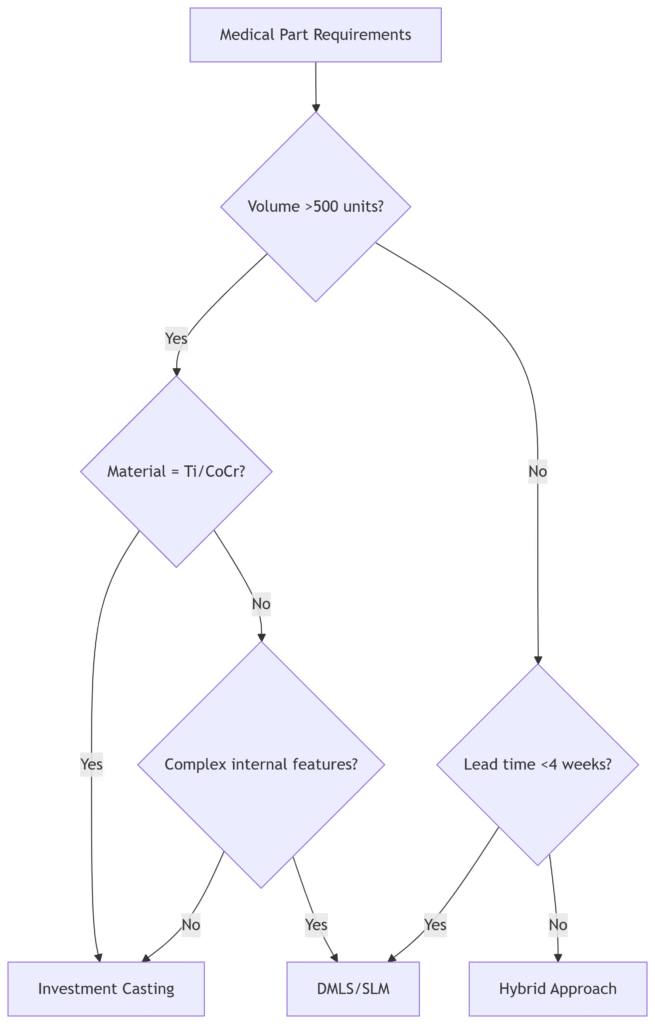
Hybrid Solution: Maximizing Benefits
Best Practices from Our FDA Projects:
- Prototype with DMLS (Accelerate design iterations)
- Production with Casting (Ensure material homogeneity)
- Critical Features Machined (Achieve <Ra 0.5μm)
Success Story:
Reduced hip implant manufacturing costs by 37% using:
- 3D printed wax patterns
- Investment casting in CoCrMo
- CNC finishing of articulation surfaces



One Response
Why Partner with Our Medical Manufacturing Team?
✔ Dedicated Cleanroom Casting (Class 8,000)
✔ Full Material Certification (Traceable to melt batch)
✔ In-House Validation Lab (Meets FDA 21 CFR Part 11)
Free Medical Manufacturing Guide Includes:
Regulatory checklist (FDA/CE/MDR)
Material selection flowchart
Surface roughness standards